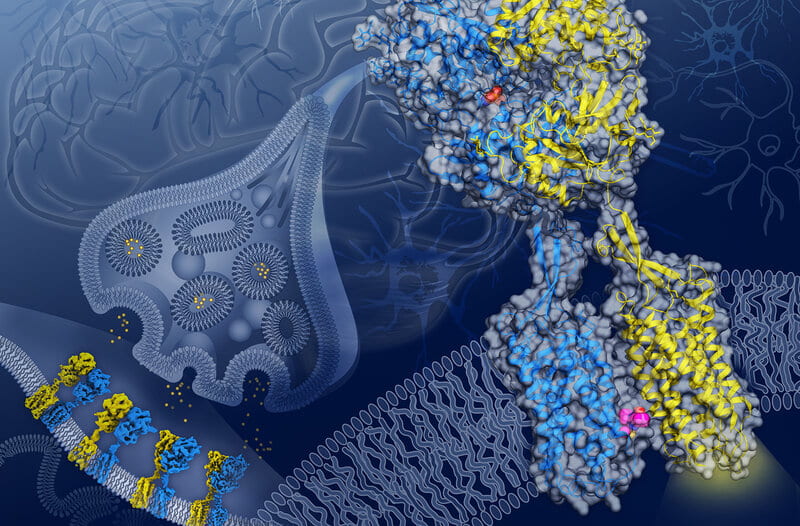
Scientists figured out how Gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA, interacts with a key protein receptor called GABAB. The study paints a clear picture of how GABA changes the shape of the GABAB protein and reveals a clear target site for new drugs. (June 17, 2020)
Scientists gain detailed images of how a protein that calms brain activity works